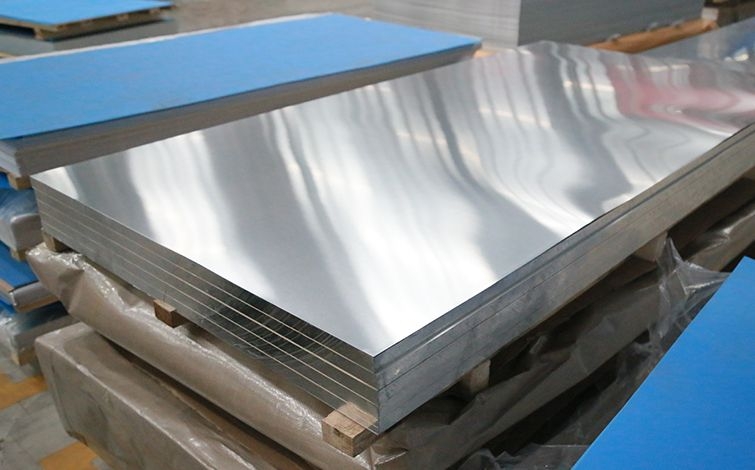



Manganese, zinc, iron and silicon in aluminium sheets
The different metallic or non-metallic components of aluminium sheets have various properties that change the original properties of the sheet and give it additional functions. So let's take a look at what manganese, zinc, iron and silicon are used for in aluminium sheets today!
Metallic elements: the influence of manganese
The maximum solubility of manganese in the solid solution is 1.82%. Al-Mn alloy long and short age-hardening alloy, that is, not heat-treatable strengthening.
Metal elements: influence of zinc
The equilibrium phase diagram of the Al-Zn alloy system is rich in aluminium sector at 275 when the solubility of zinc in aluminium is 31.6%, while at 125 its solubility drops to 5.6%. The addition of zinc to aluminium alone has a very limited progress on the strength of aluminium sheets under deformation premises, as well as a tendency to stress erosion cracking, thus limiting its application.
Metal elements: the influence of iron and silicon
Iron in the Al-Cu-Mg-Ni-Fe system of wrought aluminum alloys, silicon in the Al-Mg-Si system of wrought aluminum and in the Al-Si system of welding rods and aluminum-silicon forging alloys, are added as alloying elements, in other aluminum alloys, silicon and iron are common impurity elements, have a significant impact on the function of aluminum plate. They exist mainly as FeCl3 and free silicon. When silicon is greater than iron, β-FeSiAl3 (or Fe2Si2Al9) phase is formed, while when iron is greater than silicon, α-Fe2SiAl8 (or Fe3Si2Al12) is formed. When the ratio of iron and silicon is not appropriate, it will cause the casting to produce cracks, cast aluminum in the iron content is too high will make the casting brittle.
* Thank you for your inquiry. Please provide your business needs information so that we can better serve you.
This information can help us assign the most suitable person to solve your problem. We will give you feedback within 1-2 working days.
Related Blog







